要判断客户端是否使用代理服务器,可以从客户端所发送的环境变量信息来判断。
具体来说,就是看HTTP_VIA字段,如果这个字段设置了,说明客户端使用了代理服务器。
匿名级别可以参考下表来判断。
给出一个应用例子,可以挂上代理试试效果: http://ip.mixsec.org/
一、没有使用代理服务器的情况:
REMOTE_ADDR = 您的 IP
HTTP_VIA = 没数值或不显示
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 没数值或不显示
二、使用透明代理服务器的情况:Transparent Proxies
REMOTE_ADDR = 代理服务器 IP
HTTP_VIA = 代理服务器 IP (补充:这个字段由代理服务器填充,有时会填充网关信息等)
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 您的真实 IP
这类代理服务器还是将您的信息转发给您的访问对象,无法达到隐藏真实身份的目的。
三、使用普通匿名代理服务器的情况:Anonymous Proxies
REMOTE_ADDR = 代理服务器 IP
HTTP_VIA = 代理服务器 IP (补充:这个字段由代理服务器填充,有时会填充网关信息等)
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 代理服务器 IP
隐藏了您的真实IP,但是向访问对象透露了您是使用代理服务器访问他们的。
四、使用欺骗性代理服务器的情况:Distorting Proxies
REMOTE_ADDR = 代理服务器 IP
HTTP_VIA = 代理服务器 IP (补充:这个字段由代理服务器填充,有时会填充网关信息等)
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 随机的 IP
告诉了访问对象您使用了代理服务器,但编造了一个虚假的随机IP代替您的真实IP欺骗它。
五、使用高匿名代理服务器的情况:High Anonymity Proxies
REMOTE_ADDR = 代理服务器 IP
HTTP_VIA = 没数值或不显示
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 没数值或不显示
完全用代理服务器的信息替代了您的所有信息,就象您就是完全使用那台代理服务器直接访问对象。
除此之外,可以通过proxy judges总 结其他一些可供参考的判定信息,一遍于在实践中加以利用。
最后写一个php例子,仅供大家参考:
1 | if(!empty($_SERVER['HTTP_VIA'])) //使用了代理 |
本文为作者原创 转载时请注明出处 谢谢

乱码三千 – 点滴积累 ,欢迎来到乱码三千技术博客站














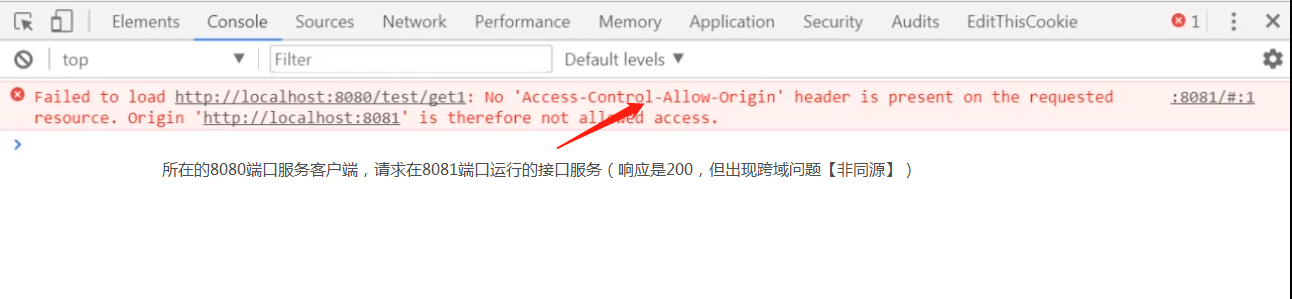
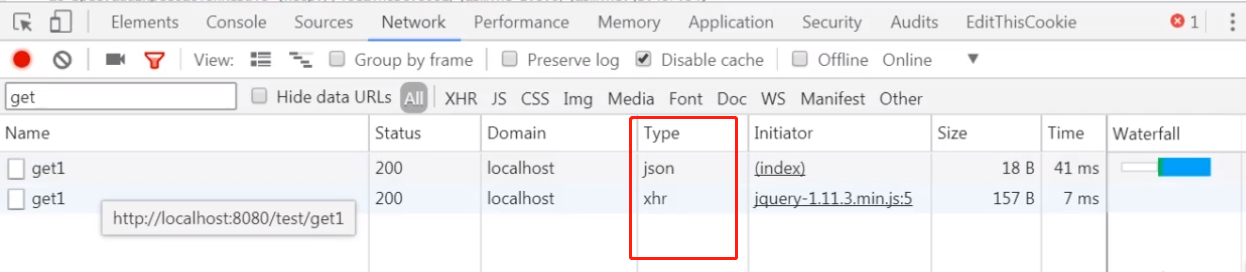
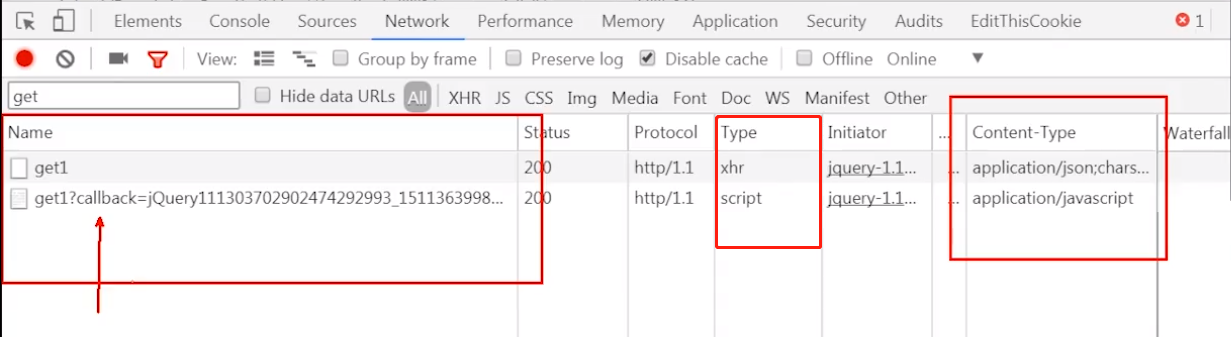
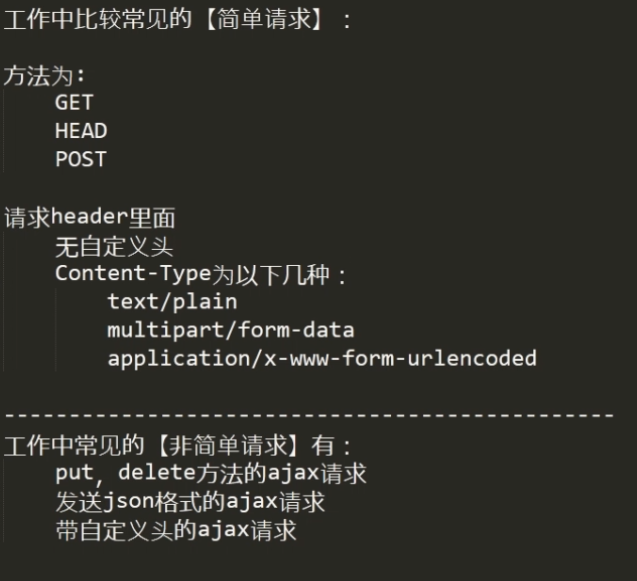







 ]
]
